Last Updated on July 5, 2021 by CHANDRAMANI
A refrigerator has become an integral part of every household. A refrigerator work on the basis of simple and interesting scientific principles.
In simple terms, the working can be understood as a basic principle in which a colder liquid i.e. refrigerant is passed around the object stored inside to be cooled this takes out heat and uses the principles of condensation and evaporation.
In order to understand the working of the refrigerator easily and properly, you must know the different components of the refrigerator and their functions.
Table of Contents
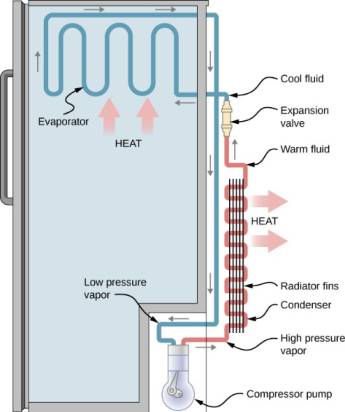
Main Components of the Refrigerator
Compressor

It raises the pressure of the refrigerant. It acts as a pump for the refrigerant and it works by raising the pressure of the refrigerant. Due to high pressure, the temperature is also increased.
Expansion Valve/Throttling Device/Capillary tube
It is a capillary tube in which cold liquid is produced in the process. The inlet refrigerant is a high-pressure liquid. This device causes obstruction to the flow of the liquid which causes a tremendous pressure drop and the boiling point of the refrigerant comes down and it evaporates. The refrigerant temperature comes down as it passes this device.
Condenser

It consists of copper tubes and is either located at the back or base of the refrigerator. It removes heat from the inside of the refrigerator. The gas from the compressor which is at high temperature and pressure is cooled down to a liquid state then travels back into the evaporator to repeat this cooling cycle.
Evaporator
The evaporator is located inside the refrigerator. It absorbs heat from inside and the refrigerant evaporates and turns into vapor. It also has a fan for circulating the cool air.
Thermostat

It is a temperature sensor that switches on and the compressor. When the internal temperature becomes equal to the desired set temperature, then the thermostat switches the compressor off and switches it on when the internal temperature rises.
Defrost Heater
Most modern refrigerator comes with an auto-defrost option. Due to moisture inside the refrigerator, the cold air leads to frost build-up on the evaporator, and as a result, it leads to inefficient cooling. A defrost heater is located below the evaporator which defrosts it.
Also read: Best Outdoor Refrigerator
How does a refrigerator work

A refrigerator works by circulating the cold liquid i.e. the refrigerant throughout it. Modern refrigerators do this by maintaining high energy efficiency.
A capillary tube is used as a throttling device. The cold liquid is produced using the throttling phenomena. The refrigerant getting inside the throttling device is at high pressure. As the refrigerant passes through the throttling device a huge drop in pressure occurs because the capillary tube offers hindrance to the refrigerant flow.
As the pressure drops the boiling point of liquid comes down and the refrigerant liquid evaporates. It is to be noted that only a portion of the refrigerant evaporates. The temperature of the refrigerant drops and you can notice this difference when you check the temperature of the start and end of the throttling device.
This refrigerant is now passed through the evaporator which runs inside the refrigerator and absorbs heat. The refrigerant inside this heat exchanger i.e. evaporator further evaporates and its temperature does not further increase as the phase change occurs.
A small fan is located near the evaporator to circulate the cold air throughout the refrigerator.
Now in order to continue this cooling effect, we have to pass this refrigerant continuously. Before the refrigerant again passes through the capillary tube i.e. evaporator its pressure must be increased.
To do so a compressor is used for this purpose. It compresses the gas and increases its pressure along with its rise in temperature. After the refrigerant comes out of the compressor it is a high-pressure vapor.
To convert it into liquid another heat exchanger i.e. a condenser is used. It liberates heat to the surroundings as it is located outside the refrigerator. The vapor condenses to liquid and the temperature reaches the normal level.
Now the refrigerant is in its initial stage and is sent to the throttling device/expansion valve/capillary tube again.
This process is repeated again and again to produce the required cooling effect and the cycle is called the vapor compression cycle.
Now you have understood the normal working of the refrigerator but this happens with some issues. The modern refrigerator overcomes them to continue functioning normally.
Common Issues faced by a Refrigerator
Frost build-up- The circulating air inside the refrigerator when it comes in contact with the cold evaporator coils, leads to frost build-up over it. The ice build-up lowers the heat transfer from the inside and makes the refrigerator inefficient. To overcome this a defrost heater is located just below the evaporator which turns on and defrosts the ice.
The modern refrigerator also shuts down its inverter compressor when the optimum internal temperature is achieved to save energy. This is done by the thermostat which when senses the optimal temperature shuts the compressor and kicks it on when the internal temperature rises.
Read Next: The Best Man Cave Refrigerators